https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/10272
M - Monster Hunter
题意:给定一棵树,有点权,每个点上有个怪物,击杀节点 u 上的怪物的代价为 u 的点权 + u 的儿子的点权和。初始时可以选择 k k k k k k
树形dp+背包
d p [ u ] [ j ] [ 1 / 0 ] dp[u][j][1/0] d p [ u ] [ j ] [ 1/0 ] u u u j j j u u u
则需要将 j j j u u u
遍历每一个儿子,更新dp数组。把一个儿子看成一种物品,每种可以拿多个,代价不同。
还要保证每层循环枚举的范围都是合法的,即不可能枚举到不存在的情况。这样每两个点只会在他们的LCA处被枚举到,复杂度就是 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O ( n 2 )
这种分配问题求最小值的应该要首先考虑背包!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(x) cout << #x << ":\t" << (x) << endl; using namespace std;#define ll long long #define ull unsigned ll const int N = 2e6 + 10 ;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f ;const ll mod = 1e9 + 7 ;int T;int n;vector<int >G[2020 ]; ll a[2020 ]; ll dp[2020 ][2020 ][2 ]; int siz[2020 ];void dfs (int u) siz[u] = 1 ; for (int v : G[u]) { dfs (v); } dp[u][0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[u][1 ][1 ] = 0 ; dp[u][0 ][1 ] = inf; dp[u][1 ][0 ] = inf; for (int v : G[u]) { siz[u] += siz[v]; for (int j = siz[u]; j >= 1 ; j--) { ll tmp1 = inf, tmp0 = inf; for (int k = max (0 , j - siz[u] + siz[v]); k <= min (j, siz[v]); k++) { tmp1 = min (tmp1, dp[u][j - k][1 ] + min (dp[v][k][0 ], dp[v][k][1 ])); tmp0 = min (tmp0, dp[u][j - k][0 ] + min (dp[v][k][0 ] + a[v], dp[v][k][1 ])); } dp[u][j][1 ] = tmp1; dp[u][j][0 ] = tmp0; } dp[u][0 ][0 ] += dp[v][0 ][0 ] + a[v]; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= siz[u]; i++)dp[u][i][0 ] += a[u]; } int main () scanf ("%d" , &T); while (T--) { scanf ("%d" , &n); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++)G[i].clear (); for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int f; scanf ("%d" , &f); G[f].push_back (i); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++)scanf ("%lld" , &a[i]); dfs (1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++)printf ("%lld%c" , min (dp[1 ][i][0 ], dp[1 ][i][1 ]), " \n" [i == n]); } return 0 ; }
H - Harmonious Rectangle
题意:一个 n ∗ m n*m n ∗ m
dfs剪枝
首先考虑如果只有一行,显然方案数为 0.
如果有两行,由鸽笼原理,最多只能有 7 列。
如果大于两行,和两行相同,最多只能有 7 列。
所以现在只需要考虑 n ≤ 7 , m ≤ 7 n\le7,m\le 7 n ≤ 7 , m ≤ 7
dfs每一格染色,只需要检查包含这格的长方形即可。
与当前格同行的某一格所在列为 j j j c 1 c1 c 1 y y y c 2 c2 c 2 j j j y y y c 1 , c 2 c1,c2 c 1 , c 2 c k [ j ] [ y ] [ c 1 ] [ c 2 ] = 0 / 1 ck[j][y][c1][c2]=0/1 c k [ j ] [ y ] [ c 1 ] [ c 2 ] = 0/1 j j j y y y c 1 , c 2 c1,c2 c 1 , c 2
如果与当前格同行的某一格的颜色与当前格相同,则还需要判断这两列是否在某一行颜色相同。
注意还要把答案存起来,防止重复询问。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(x) cout << #x << ":\t" << (x) << endl; using namespace std;#define ll long long #define ull unsigned ll const int N = 2e6 + 10 ;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f ;const ll mod = 1e9 + 7 ;int T;int n, m;ll Pow (ll a, ll b) { a %= mod; ll res = 1 ; while (b) { if (b & 1 )res = res * a%mod; a = a * a%mod; b >>= 1 ; } return res; } int a[10 ][10 ], ans[10 ][10 ];int ck[10 ][10 ][4 ][4 ];void dfs (int x, int y) if (x > n) { ans[n][m] = (ans[n][m] + 1 ) % mod; return ; } for (int c = 1 ; c <= 3 ; c++) { bool flg = 1 ; for (int j = 1 ; j < y && flg; j++) { if (a[x][j] == c) { if (ck[j][y][1 ][1 ] || ck[j][y][2 ][2 ] || ck[j][y][3 ][3 ])flg = 0 ; } if (ck[j][y][a[x][j]][c])flg = 0 ; } if (!flg)continue ; a[x][y] = c; for (int j = 1 ; j < y; j++) { ck[j][y][a[x][j]][c] = 1 ; } int nx = x, ny = y + 1 ; if (ny > m)ny = 1 , nx++; dfs (nx, ny); for (int j = 1 ; j < y; j++) { ck[j][y][a[x][j]][c] = 0 ; } } } int main () memset (ans, -1 , sizeof scanf ("%d" , &T); while (T--) { scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); if (min (n, m) == 1 ) { puts ("0" ); continue ; } if (max (n, m) > 7 ) { printf ("%lld\n" , Pow (3 , n*m)); continue ; } if (~ans[n][m]) { printf ("%d\n" , ans[n][m]); continue ; } ans[n][m] = 0 ; dfs (1 , 1 ); ans[n][m] = (Pow (3 , n*m) - ans[n][m] + mod) % mod; printf ("%d\n" , ans[n][m]); } return 0 ; }
但是事实证明只要考虑到“每次只需要检查当前格所在长方形”,再枚举长方形对角的顶点,同样要加上存答案的数组,两层循环也是可以过的。甚至时间还快一点。0.o
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(x) cout << #x << ":\t" << (x) << endl; using namespace std;#define ll long long #define ull unsigned ll const int N = 2e6 + 10 ;const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f ;const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f ;const ll mod = 1e9 + 7 ;int T;int n, m;ll Pow (ll a, ll b) { ll res = 1 ; while (b) { if (b & 1 )res = res * a%mod; a = a * a%mod; b >>= 1 ; } return res; } int a[10 ][10 ];ll ans[10 ][10 ]; typedef pair<int , int >pii;void dfs (int x, int y) if (x > n) { ans[n][m] = (ans[n][m] + 1 ) % mod; return ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= 3 ; i++) { a[x][y] = i; bool flg = 1 ; for (int i = 1 && flg; i < x; i++) { for (int j = 1 ; j < y && flg; j++) { if (a[i][j] == a[i][y] && a[x][j] == a[x][y] || a[i][j] == a[x][j] && a[i][y] == a[x][y])flg = 0 ; } } if (!flg)continue ; int nx = x, ny = y + 1 ; if (ny > m)ny = 1 , nx++; dfs (nx, ny); } } int main () memset (ans, -1 , sizeof scanf ("%d" , &T); while (T--) { scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &m); if (min (n, m) == 1 ) { puts ("0" ); continue ; } if (max (n, m) > 7 ) { printf ("%lld\n" , Pow (3 , n*m)); continue ; } if (~ans[n][m]) { printf ("%lld\n" , ans[n][m]); continue ; } ans[n][m] = 0 ; dfs (1 , 1 ); ans[n][m] = (Pow (3 , n*m) - ans[n][m] + mod) % mod; printf ("%lld\n" , ans[n][m]); } return 0 ; }
A - Ah, It’s Yesterday Once More
题意:要求构造一个n,m都不超过20的迷宫,可以有不能走的墙和空格子。每个空格子里有一个人可以上下左右走,但如果走的方向是墙,则不动。现在随机一个长度为 5 e 4 5e4 5 e 4 25 % 25\% 25%
构造
玄学题
参见题解构造
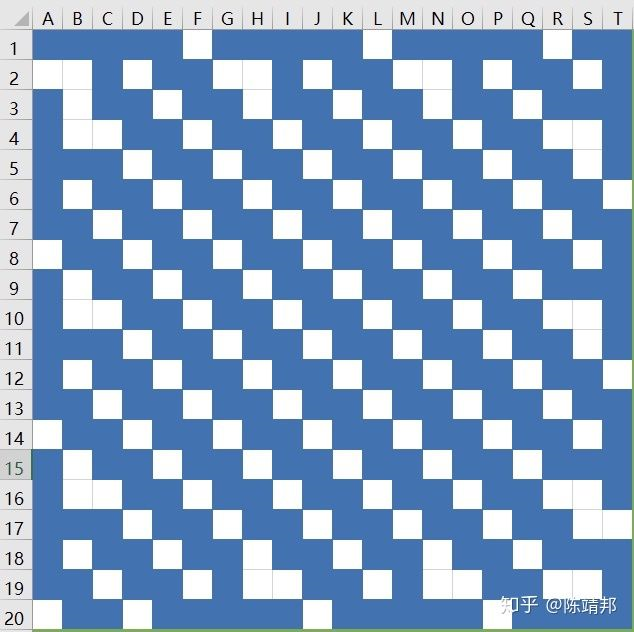
白色是墙,蓝色是空格子。
下面代码是另一种构造。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 20 20 01000111000111000111 11101101101101101101 10110110110110110110 11011011011011011011 01101101101101101101 00110110110110110111 01011011011011011010 11101101101101101100 10110110110110110110 11011011011011011011 01101101101101101101 00110110110110110111 01011011011011011010 11101101101101101100 10110110110110110110 11011011011011011011 01101101101101101101 10110110110110110111 11011011011011011010 01110001110001110000
J - Just Another Game of Stones
题意:n n n x x x [ l , r ] [l,r] [ l , r ] max ( a i , x ) \max(a_i,x) max ( a i , x ) [ l , r ] [l,r] [ l , r ] x x x
势能线段树+尼姆游戏
假设现在玩一个确定的尼姆游戏,异或和为 x x x a i ⊕ x < a i a_i\oplus x<a_i a i ⊕ x < a i
而通过分类讨论能够发现,如果 a i a_i a i x x x
所以现在变成询问某个区间的异或和。且有区间变max操作。
区间取min,max用势能线段树。
在不同线段树的基础上加上区间最小值和次小值,只处理最小值小于x,而次小值大于x的情况,即每次只更新等于最小值的位置。
对于本题再维护区间中每一个二进制位中 1 的个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug(x) cout << #x << ":\t" << (x) << endl; using namespace std;#define ll long long #define ull unsigned ll const int N = 2e6 + 10 ;const int INF = 0x7f3f3f3f ;const ll inf = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f ;const ll mod = 1e9 + 7 ;int n, q;int a[N];#define mid ((l+r)>>1) #define lson l,mid,rt<<1 #define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1 int trmn[N << 2 ], trsmn[N << 2 ], trcmn[N << 2 ], trsum[N << 2 ][30 ], laz[N << 2 ];void up (int rt) if (trmn[rt << 1 ] == trmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]) { trmn[rt] = trmn[rt << 1 ]; trcmn[rt] = trcmn[rt << 1 ] + trcmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]; trsmn[rt] = min (trsmn[rt << 1 ], trsmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]); } else if (trmn[rt << 1 ] < trmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]) { trmn[rt] = trmn[rt << 1 ]; trcmn[rt] = trcmn[rt << 1 ]; trsmn[rt] = min (trsmn[rt << 1 ], trmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]); } else { trmn[rt] = trmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]; trcmn[rt] = trcmn[rt << 1 | 1 ]; trsmn[rt] = min (trsmn[rt << 1 | 1 ], trmn[rt << 1 ]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++)trsum[rt][i] = trsum[rt << 1 ][i] + trsum[rt << 1 | 1 ][i]; } void pushtag (int x, int l, int r, int rt) if (x <= trmn[rt])return ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++) { if (trmn[rt] >> i & 1 )trsum[rt][i] -= trcmn[rt]; if (x >> i & 1 )trsum[rt][i] += trcmn[rt]; } trmn[rt] = laz[rt] = x; } void down (int l, int r, int rt) int & x = laz[rt]; if (x) { pushtag (x, lson); pushtag (x, rson); x = 0 ; } } void build (int l, int r, int rt) if (l == r) { trmn[rt] = a[l]; trsmn[rt] = INF; trcmn[rt] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++) { trsum[rt][i] = (a[l] >> i & 1 ); } return ; } build (lson); build (rson); up (rt); } void upd (int ql, int qr, int x, int l, int r, int rt) if (trmn[rt] >= x)return ; if (ql <= l && qr >= r && trsmn[rt] > x) { pushtag (x, l, r, rt); return ; } down (l, r, rt); if (ql <= mid)upd (ql, qr, x, lson); if (qr > mid)upd (ql, qr, x, rson); up (rt); } int cnt[30 ];void qry (int ql, int qr, int l, int r, int rt) if (ql <= l && qr >= r) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++)cnt[i] += trsum[rt][i]; return ; } down (l, r, rt); if (ql <= mid)qry (ql, qr, lson); if (qr > mid)qry (ql, qr, rson); } int main () scanf ("%d%d" , &n, &q); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++)scanf ("%d" , &a[i]); build (1 , n, 1 ); while (q--) { int op, l, r, x; scanf ("%d%d%d%d" , &op, &l, &r, &x); if (op == 1 ) { upd (l, r, x, 1 , n, 1 ); } else { memset (cnt, 0 , sizeof qry (l, r, 1 , n, 1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < 30 ; i++) { cnt[i] += (x >> i & 1 ); } bool flg = 0 ; for (int i = 29 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { if (cnt[i] & 1 ) { printf ("%d\n" , cnt[i]); flg = 1 ; break ; } } if (!flg)puts ("0" ); } } return 0 ; }